Categories
What Is Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring: Reliable & Accurate Blood Pressure 24/7

Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, or simply ABPM, is a relatively new and non-invasive method or technique of obtaining a patient’s blood pressure readings 24/7, while a patient stays in his/her own environment and represents a true blood pressure reflection. In the simplest terms, ABPM assesses or measures a patient’s blood pressure at regular intervals (every 20 minutes at daytime, every hour overnight). A device used for ABPM is called ambulatory blood pressure machine or monitor.
Many medical studies have already confirmed that 24/7 ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is superior to blood pressure monitoring in a clinical setting in estimating cardiac risk factors, like predicting future target organ damage and cardiovascular events. ABPM is able to provide the information that will be fundamentally different from the one got by a doctor out of a patient’s blood pressure readings taken in the office. For example, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is believed to be helpful in reducing the effect of white coat hypertension, according to which a patient’s blood pressure gets elevated during a medical examination as a response to a simple anxiety or nervousness caused by being in a clinical environment. For this reason almost all hypertension organizations highly recommend to use ABP or out-of-office measurements as an adjunct to office measurements. Let’s take a deeper look at the main guidelines of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring technique.
Contents
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Guidelines: What Can ABPM Be Used For?
In the medical community ABPM is recognized as a valuable supporting tool of an appropriate pharmacologic treatment management and can have the following uses:
- to measure increased blood pressure readings, which are more reliable and accurate and more strongly correlated to target organ damage or cardiovascular events than one-off measurements;
- to detect the effect of white coat hypertension (blood pressure readings recorded in the physician’s office are elevated, but normal when recorder outside it);
- to assess resistant hypertension (anti-hypertensive medications fail to properly control high blood pressure);
- to assess masked hypertension (when measurements are within an acceptable range, but the blood pressure is actually above it);
- to assess hypotensive symptoms while on hypertensive medications;
- to be used in hypertension or prognostic research;
- to assess episodic or autonomic dysfunction.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Device: Speaking Of ABPM-Referred Patients & ABPM Diagnostic Test
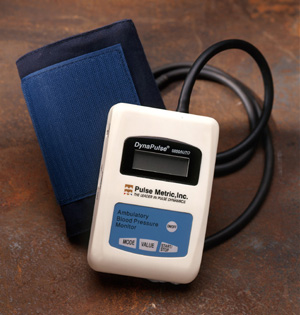
Ambulatory blood pressure monitor is a diagnostic device that consists of BP cuff attached to a portable monitor (CD-player-size recording device), which is worn on a belt. ABPM is strongly recommended for patients with either labile or persistently raised blood pressure readings, patients susceptible to reversed-type or ordinary white coat hypertension, patients that are at high risk of target organ damage or cardiovascular events developing, etc.
The principles of ABPM diagnostic test are simple. It begins with fitting a patient with a BP cuff and a portable monitor that is worn from 24 to 48 hours and which records or takes your blood pressure measurements periodically or at regular intervals (usually every 15-30 minutes when awake and every 30-60 minutes when asleep). In general, ABPM results will provide a doctor with the most complete representation of a patient’s blood pressure profile.



